Preventive health simplified
Healthdom helps prevent illness by providing you with personalized screenings and check-up plans based on your DNA, wearables, lifestyle and medical history.
Sign up todayAre you protecting the life you love and staying healthy?
The current healthcare system is reactive and complex. Be proactive today to prevent problems down the road.
Avoid those problems by right screenings at the right time and healthier lifestyle.
How well are you protecting your health?
Free assessment within 5 minutes
Getting started is easy and free
Just follow these three simple steps:
1. Take health assessment and DNA test
Short online health risk assessment (~5 min) and optional DNA test to get a deep understanding of your health determinants.
2. Discover your health action plan
Instantly receive 360° analysis including benchmarks around your health. Within 24 hours get an individualized plan with a score of how well you are protecting your health.
3. Enjoy simplified management of your health
Centralize your medical records, manage your health-related tasks and optimize your screening schedule.
see more…
Effortlessly stay on top of your health,
securely and affordably
Cut through the noise
Our team of medical experts and professionals have carefully curated the content to simplify medical jargon. Our recommendations are strictly based on well-established medical guidelines. You can find sources to all our recommendations and content within the product. We believe in transparency and clearly explain why a recommendation is relevant to you.
Working along with your doctor
Typically, doctors spend 10-min or less with a patient during a visit. Healthdom gives you additional leverage and resources to organize all your screenings and tests so that when you are with your doctor, you can spend time more effectively. We complement your physician visit with additional prevention methods (e.g. genomics and behavioral data), to ensure comprehensive health management.


Low-cost prevention
The US Affordable Care Act makes the majority of preventive tests free, and Healthdom helps you access this benefit. For tests that are not free, we provide access to the most affordable provider so that you can save.
Minimizing health deterioration through awareness
We understand that your health data is highly personal and private. Healthdom uses industry-standard security and encryption method to protect your data. We are HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act ) compliant and do not share your individual-level information with any third-party without your explicit consent. Additionally, we will delete your individual health data from our systems if you ever request it.
Effortlessly stay on top of your health,
securely and affordably

Cut through the noise
Our team of medical experts and professionals have carefully curated the content to simplify medical jargon. Our recommendations are strictly based on well-established medical guidelines. You can find sources to all our recommendations and content within the product. We believe in transparency and clearly explain why a recommendation is relevant to you.
Working along with your doctor
Typically, doctors spend 10-min or less with a patient during a visit. Healthdom gives you additional leverage and resources to organize all your screenings and tests so that when you are with your doctor, you can spend time more effectively. We complement your physician visit with additional prevention methods (e.g. genomics and behavioral data), to ensure comprehensive health management.
Low-cost prevention
The US Affordable Care Act makes the majority of preventive tests free, and Healthdom helps you access this benefit. For tests that are not free, we provide access to the most affordable provider so that you can save.
Minimizing health deterioration through awareness
We understand that your health data is highly personal and private. Healthdom uses industry-standard security and encryption method to protect your data. We are HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act ) compliant and do not share your individual-level information with any third-party without your explicit consent. Additionally, we will delete your individual health data from our systems if you ever request it.
Examples of how Healthdom
can help you
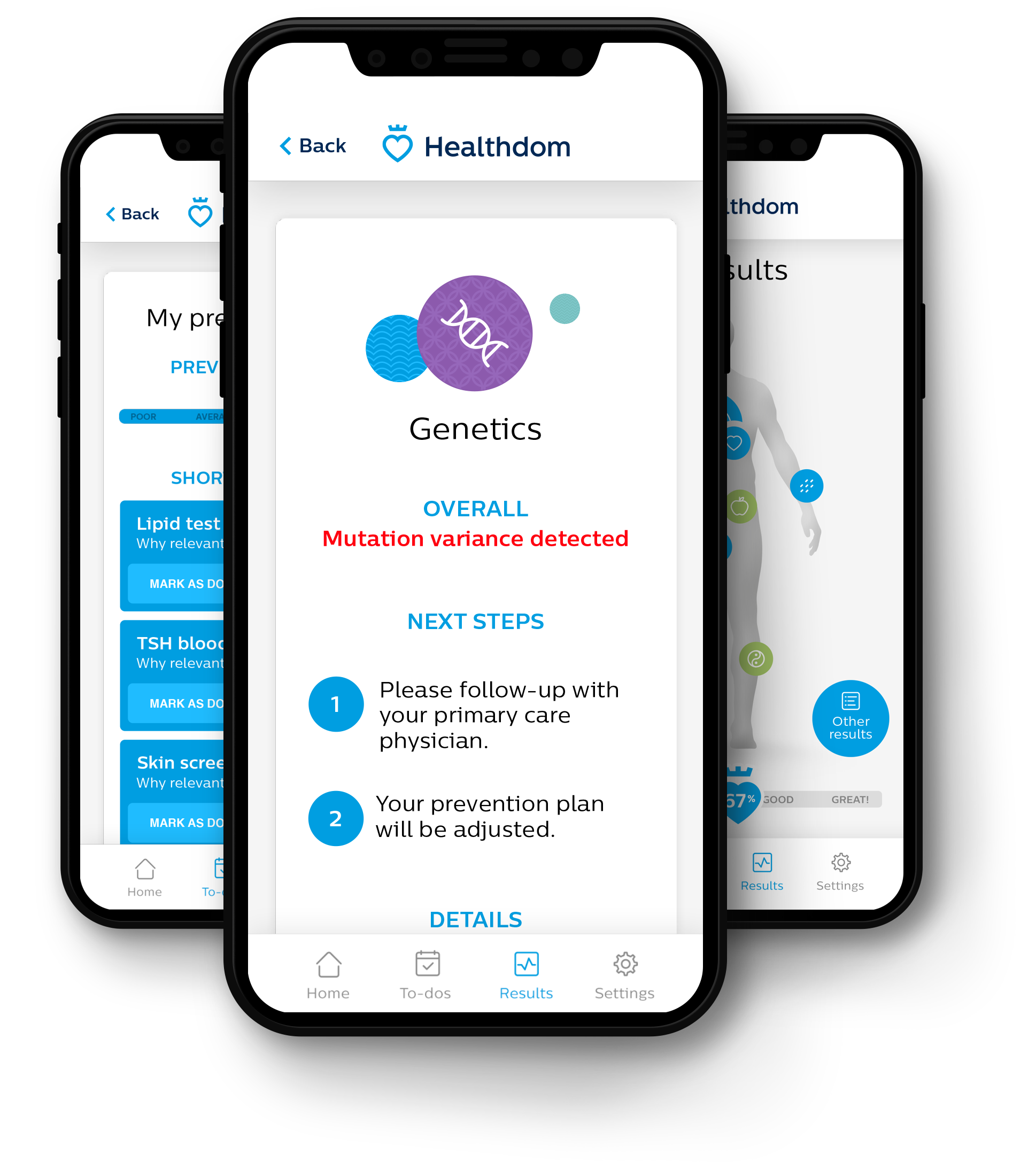
Increasing your chances against breast cancer
If you are a woman with a BRCA1/2 gene mutation (which indicates breast cancer susceptibility) you might not know about it until the cancer is advanced. With Healthdom, you might learn about the mutation early and get a recommendation for increased monitoring. This early detection could lead to your best chances of successful treatment.Triggering diet change based on DNA test
If you had hemochromatosis (too much iron in the blood) you might not know it until later in life. But by that time, the damage done might be irreversible and result in liver cirrhosis. Healthdom might discover the disease upfront, suggesting that you change your diet and start regular phlebotomy, which can help you lead a normal life.Reducing colorectal cancer risk
If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, you would most likely postpone preventive colonoscopies until you were 55. But for some people, 55 is too late, and cancer might already develop. If your family history survey shows hereditary risk, the Healthdom algorithm would prompt you to get tested much earlier, giving you the option for early care. Our news
Examples of how Healthdom
can help you
Increasing your chances against breast cancer
If you are a woman with a BRCA1/2 gene mutation (which indicates breast cancer susceptibility) you might not know about it until the cancer is advanced. With Healthdom, you might learn about the mutation early and get a recommendation for increased monitoring. This early detection could lead to your best chances of successful treatment.
Triggering diet change based on DNA test
If you had hemochromatosis (too much iron in the blood) you might not know it until later in life. But by that time, the damage done might be irreversible and result in liver cirrhosis. Healthdom might discover the disease upfront, suggesting that you change your diet and start regular phlebotomy, which can help you lead a normal life.
Reducing colorectal cancer risk
If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, you would most likely postpone preventive colonoscopies until you were 55. But for some people, 55 is too late, and cancer might already develop. If your family history survey shows hereditary risk, the Healthdom algorithm would prompt you to get tested much earlier, giving you the option for early care. Our news
Our news

Brain First: How Preventive Medicine Protects Cognitive Health from Alzheimer’s and Dementia
A narrative exploration of the neurobiology of aging, detailing the glymphatic system, the concept of 'Type 3 Diabetes’, and how multimodal interventions can build cognitive reserve.
03/13/2026

Sarcopenia and Metabolic Plasticity: Muscle as a Secretory Endocrine Organ
A deep clinical review of skeletal muscle’s role in glucose disposal, myokine signaling, and longevity, challenging the view of muscle as merely 'locomotive tissue’.
02/11/2026

Advanced Biomarkers: The Genomic and Proteomic Frontier of Preventive Diagnostics
A comprehensive analysis of the shift from population-based reference ranges to personalized metabolic profiling, detailing the mechanisms of ApoB, Lp(a), and inflammatory cytokines.
01/23/2026

Brain First: How Preventive Medicine Protects Cognitive Health from Alzheimer’s and Dementia
A narrative exploration of the neurobiology of aging, detailing the glymphatic system, the concept of 'Type 3 Diabetes’, and how multimodal interventions can build cognitive reserve.
03/13/2026

Sarcopenia and Metabolic Plasticity: Muscle as a Secretory Endocrine Organ
A deep clinical review of skeletal muscle’s role in glucose disposal, myokine signaling, and longevity, challenging the view of muscle as merely 'locomotive tissue’.
02/11/2026

Advanced Biomarkers: The Genomic and Proteomic Frontier of Preventive Diagnostics
A comprehensive analysis of the shift from population-based reference ranges to personalized metabolic profiling, detailing the mechanisms of ApoB, Lp(a), and inflammatory cytokines.
01/23/2026